Week 6 - Introduction to Binary Exploitation
Never Trust User Input!
- Human
- Human errors
- Insider threat
- Social engineering
- Indifference
- Application <- This is what binary exploitation exploits
- Functions
- Storage
- Memory Management
- Input validation
- Host
- Access control
- Memory
- Malware
- Backdoor
- OS/Kernel
- Network
- Map the network
- Services
- Leaks
- Intercept Traffic
Commands:
- find - Search for files in a directory
- locate - Find Files by name, quickly
- which - locate a command
Finding SUID Files:
find / -perm -4000 or find / -perm -u=s -type f
Finding SGUID Files:
find / -perm -2000 or find / -perm -g=s -type f
Finding SUID + SGID:
find / -perm -6000 or find / -perm -u+g=s -type f
Read files:
- cat
- strings
- xxd
Manipulate files:
- vi
Compilation for C Programs:
- gcc
- gcc-multilib
Read Binary File Objects/Locations:
- objdump
- dmesg
Read Memory:
- gdb
- gdb-peda
Exploit Development:
- python3
- Any Programming language really
- Sequential bytes
- Instructions/Code
- Data
- EXE - Windows
- ELF - Linux
- 32-bits - 4 bytes
- 64-bits - 8 bytes
When a program is executed it is loaded into memory.
- Registers
- Quickly accessible location on the computer’s processor
- Code
- Stack
- Heap
Size:
- 8 bit
- 32 bit
- 64 bit
Types:
- General
- Data
- Pointers
- Index
- Control
- Segment
- (E/R)AX - Accumulator: Arithmetic Instructions
- (E/R)BX - Base Register: Indexed Addressing
- (E/R)CX - Count Register: Stores counts in iterative operations e.g. Loops
- (E/R)DX - Data Register
AX - 8 Bits
EAX - 32 Bits
RAX - 64 Bits
- IP - Instruction Pointer: Stores the offset address of the next instruction to be executed
- SP - Stack Pointer: Provides offset value within the program stack
- BP - Base Pointer: Referencing a parameter within a subroutine
-
A buffer, or data buffer is an area of physical memory storage used to temporarily store data
-
The challenge is when the data that is entered into the buffer extends beyond the intended location
-
A Buffer Overflow will cause the program to crash
-
Can be manipulated to
- Run Unintended functions
- Run inputted code
-
Types:
- Stack-Based: overflow a buffer on the call stack
- Heap-Based: attacks target data in the open memory pool known as the heap
- Integer Overflow
- Unicode Overflow
When a binary file is executed, it is loaded into memory.
The stack saves temporary data:
- Function parameters
- Local variables
- Function Calls
The stack is last in first out.
Data is Pushed onto the stack and Popped off
Some Vulnerable C Functions:
- gets
- strcpy
- scanf
- Many more
- All inputs, string functions are potentially vulnerable to an attack
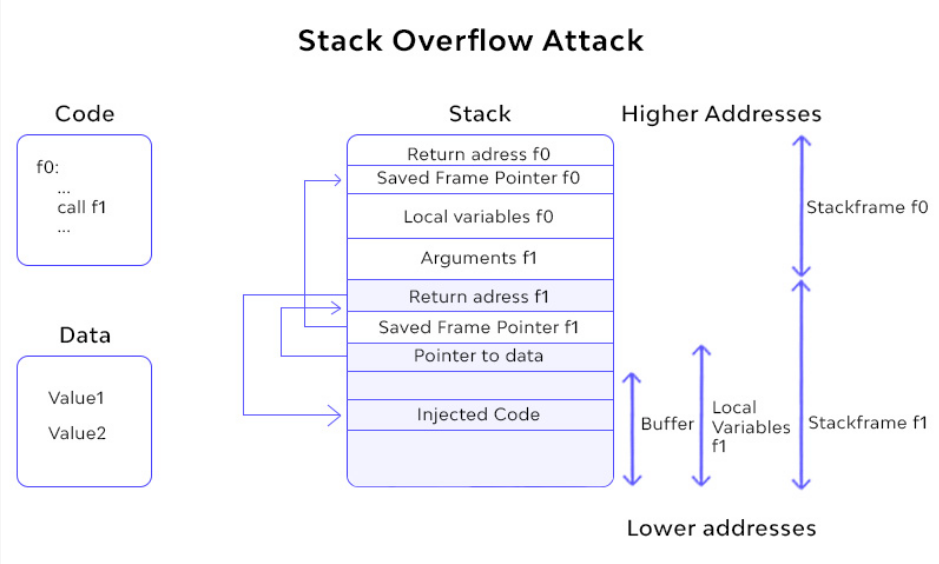
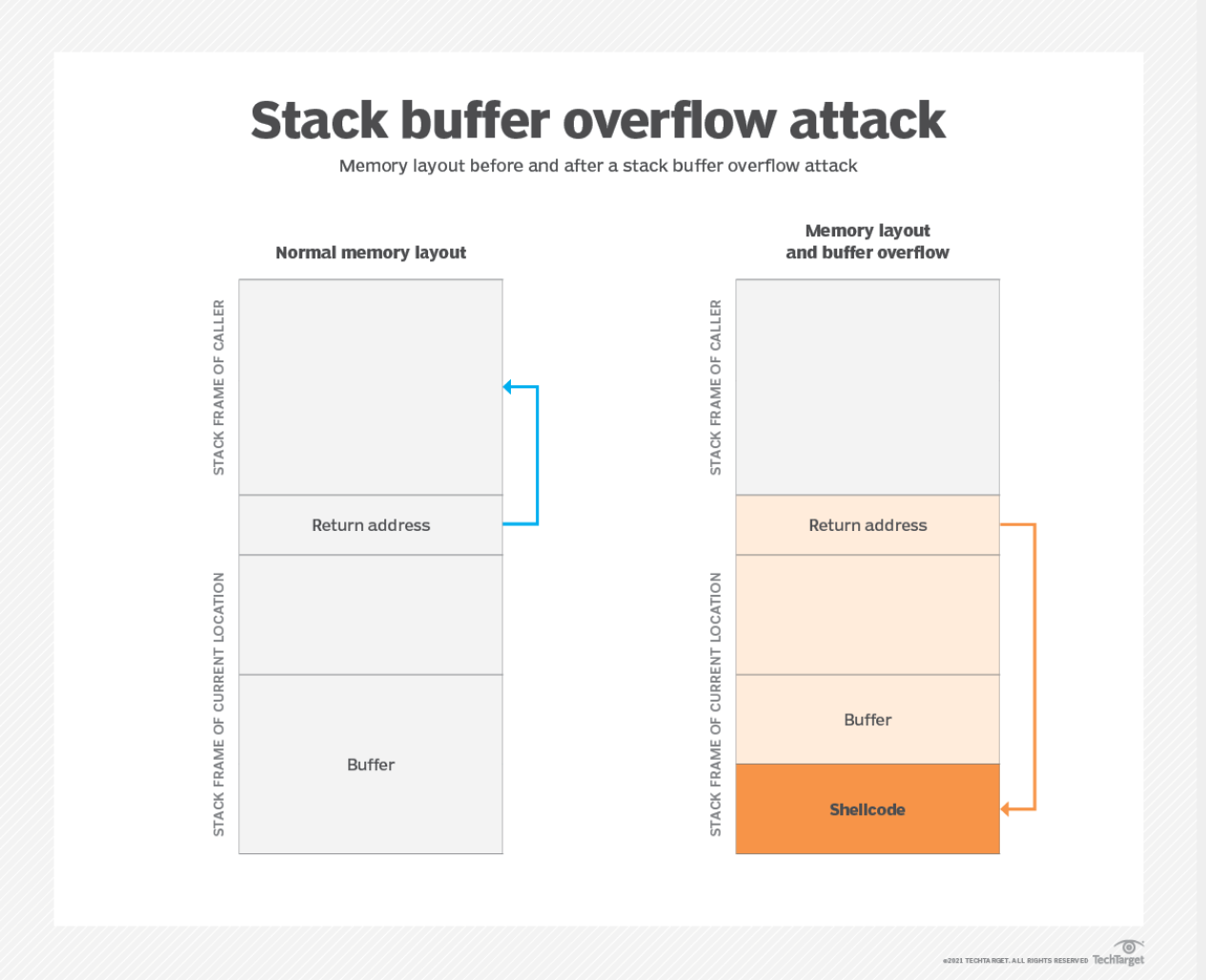
Defences:
- Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR)
- Data Execution Protection
- Structured Exception Handling
- Patch devices/software
- Safe Programming
- Validating data
- Least privilege